
Monocular depth estimation is crucial for robotics, of-fering a lightweight and scalable alternative to stereo or LiDAR-based systems. While recent methods have achieved high accuracy, their efficacy degrades under real-world conditions such as occlusion, and domain shifts. We introduce ConFiDeNet, a unified framework that jointly predicts metric depth and associated aleatoric uncertainty, enabling risk-aware robotic perception. ConFiDeNet employs a lightweight parallel attention module that efficiently fuses semantic cues from DINOv2 dense descriptors and SAM2- based segmentation for densely occluded objects, enhancing structural understanding without sacrificing real-time performance. Further, we explicitly condition the model on environment type, improving generalization across diverse indoor and outdoor scenes without retraining. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results across six datasets under both supervised and zero-shot settings, outperforming nine prior techniques, including Marigold, ZoeDepth, PatchFusion, and MonoProb. With significantly faster inference and high prediction confidence, ConFiDeNet is readily deployable for embodied AI, self-driving applications, and robotic manipulation tasks. We will release the code and models.
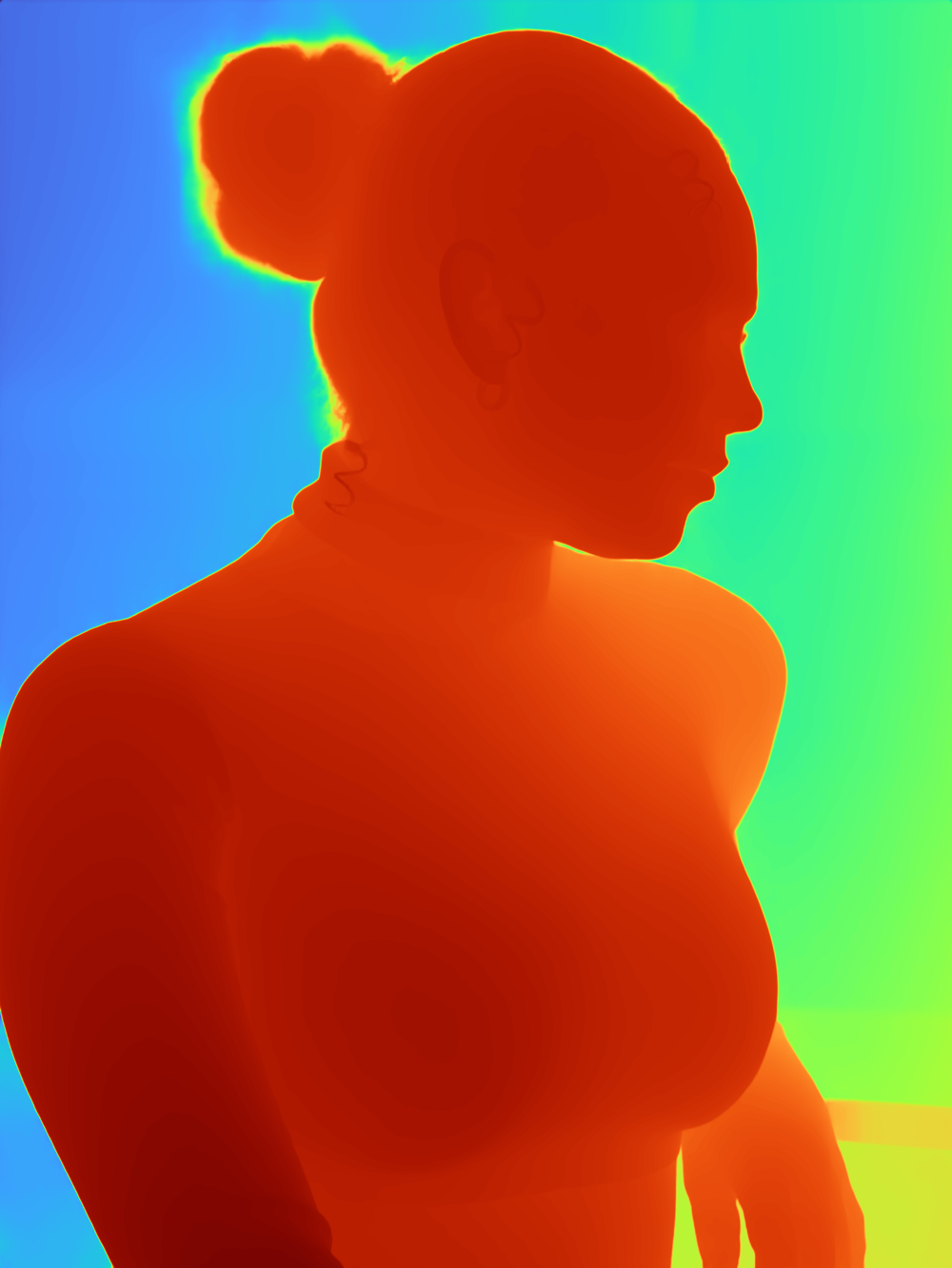


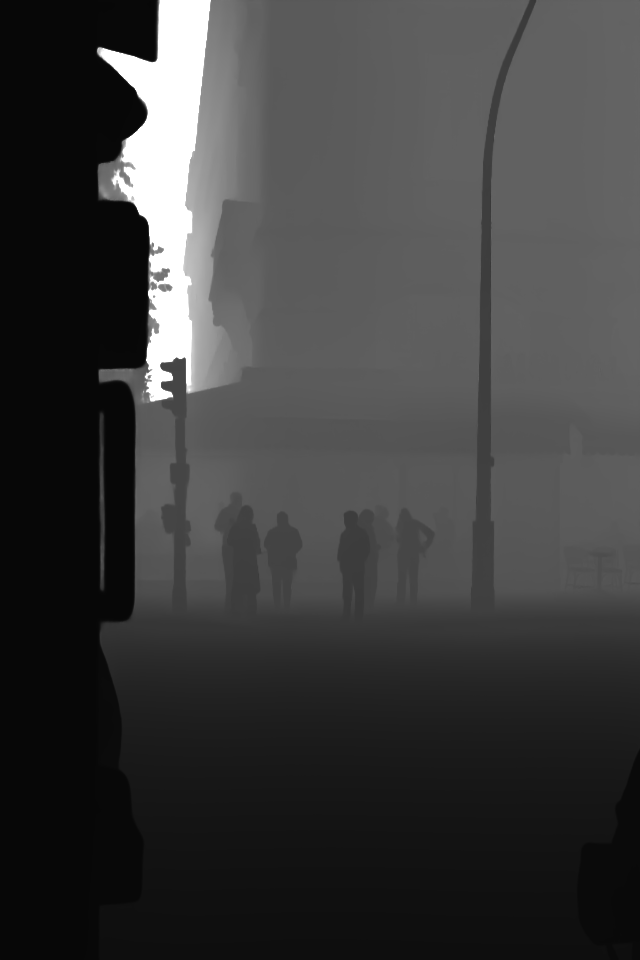

















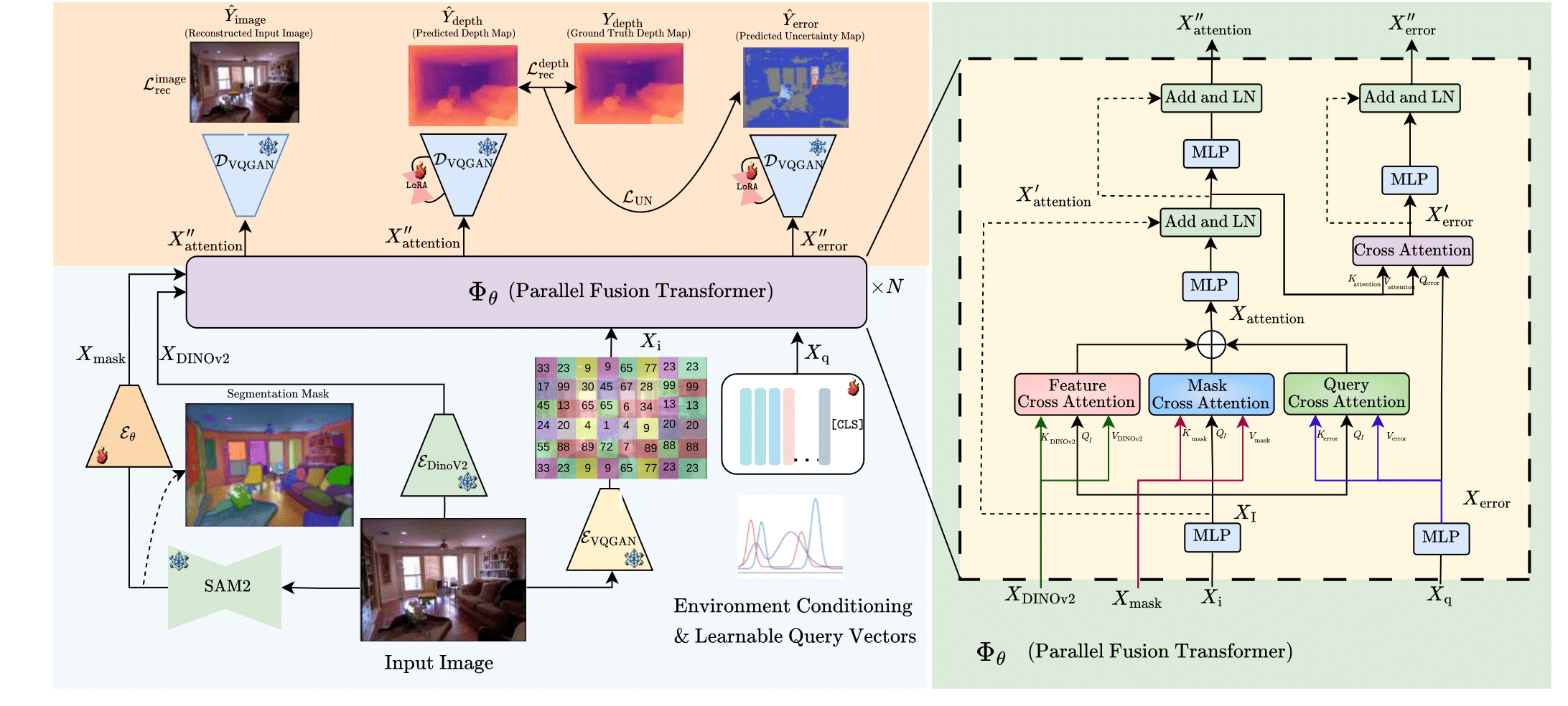
The method first extracts a semantic mask from the input image using SAM2 and obtains rich visual features using DINOv2. These features, along with VQGAN-encoded image tokens and learnable environment-query vectors, are fused inside a Parallel Fusion Transformer, where separate cross-attention modules blend feature, mask, and query information. The refined representations are then decoded through LoRA-enhanced VQGAN decoders to produce the depth map, uncertainty map, and an auxiliary reconstructed image. Training uses a combination of depth reconstruction loss, uncertainty loss, and image reconstruction loss for stable and reliable depth estimation.
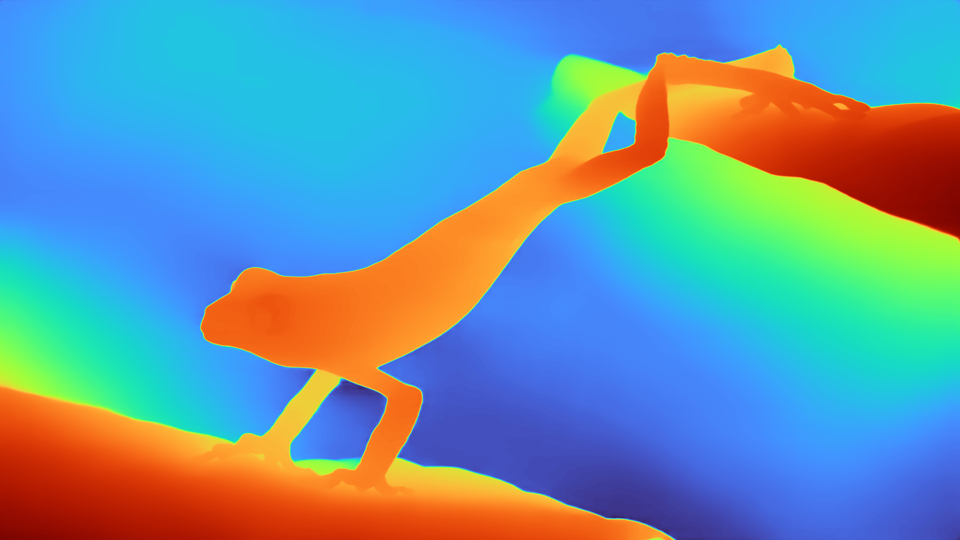
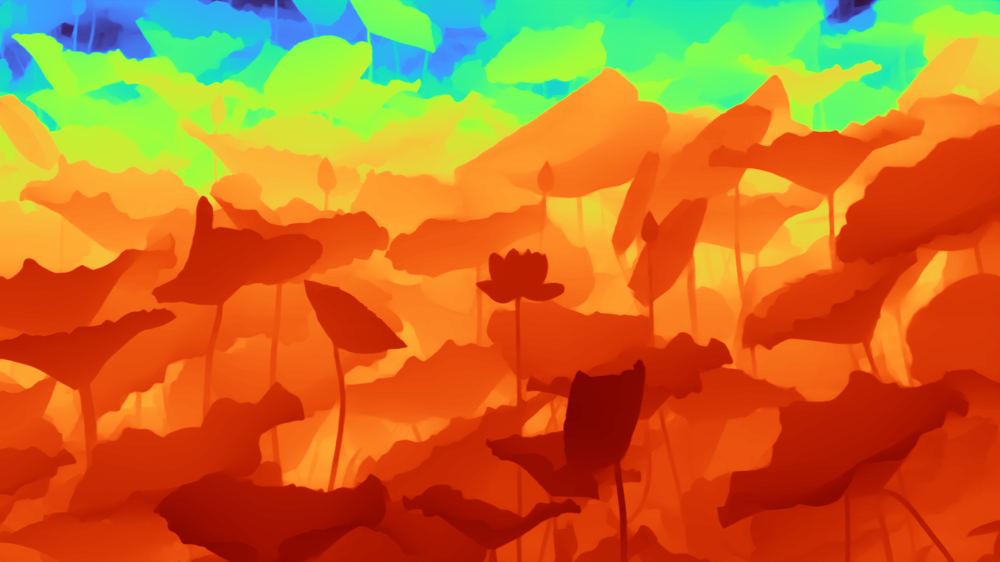
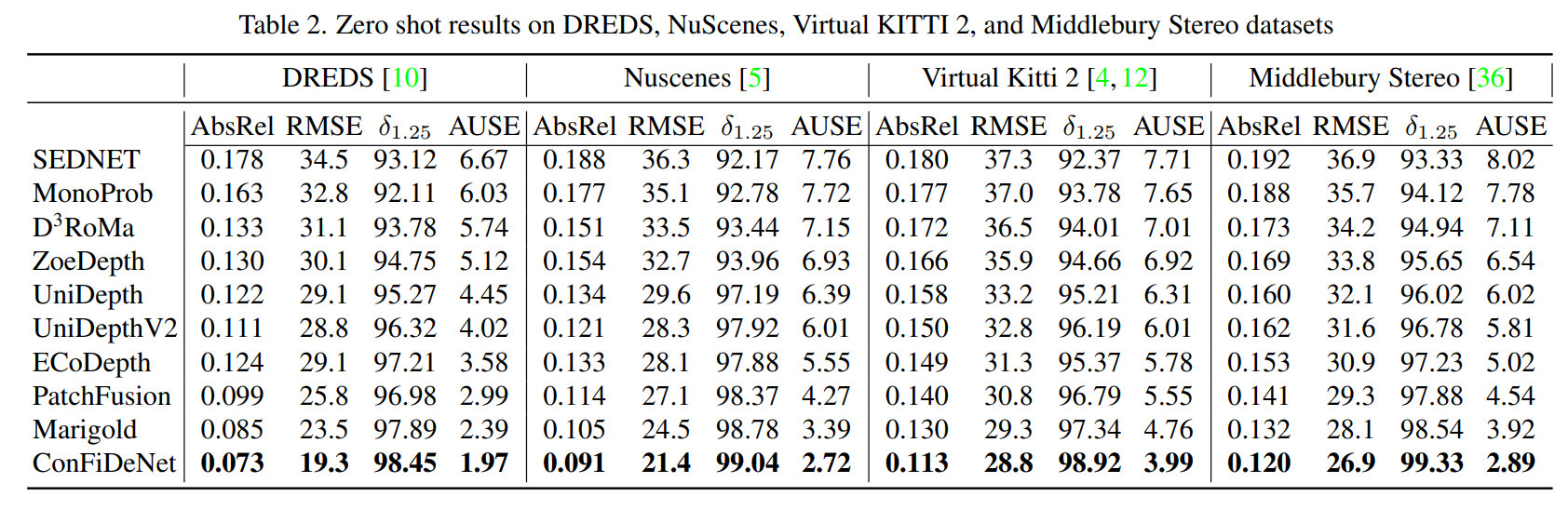
Our model surpasses baselines on all key metrics on all datasets. It outperforms Marigold on variance reduction and ECoDepth on robustness under occlusions. The Virtual KITTI 2 results highlight that ConFiDeNet has strong synthetic-to-real generalization, outperforming methods like PatchFusion and Marigold without requiring domain adaptation. Despite the monocular-tostereo modality shift in the Middlebury Stereo dataset, ConFiDeNet maintains accurate high-resolution depth estimation. Across both indoor and outdoor datasets, our model achieves the highest average δ1.25 of 99.01%, indicating highly reliable depth predictions. Additionally, we obtain the lowest AUSE, confirming that our uncertainty maps are well-calibrated and effectively identify erroneous regions.
Refer to the pdf paper linked above for more details on qualitative, quantitative, and ablation studies.